The Weekly Deep Dive: Solar Power
In episode 69 of the Who's Saving the Planet Podcast, Lex Kiefhaber and Tony Noto chat with Yaniv Kalish about all things solar power. Yaniv is the CEO and founder of SolarKal, a solar advisory service that simplifies the switch from non-renewable energy consumption to solar energy. In doing so, Yaniv has made solar energy a far more accessible option to a wider market, paving the way to a clean energy future.
Make sure to listen to Yaniv here!
Below we dive deeper into the topic of solar power, finding out what it actually is, how we generate it efficiently, and which country is dominating the solar power industry!
What is solar power?
Solar energy comes from the sun and reaches Earth in the form of electromagnetic rays. Consequently, almost all of the energy available at Earth’s surface comes from the sun, creating a warm and hospitable environment for life to flourish. This solar energy can be converted into thermal or electrical energy that we can use in replacement of fossil fuels. Solar energy is a highly sustainable resource as it is clean, highly abundant, and inexhaustible, unlike fossil fuels which are finite and pollute the environment.
How do we harness solar power?
Solar energy can be harnessed in a variety of ways.
1. Photovoltaic cells
Photovoltaic cells can be found on small gadgets such as calculators and watches or, more commonly, are grouped together to create solar panels, which are typically fitted to the roofs of buildings.

[Image sourced from InterMountain Wind & Solar].
Photovoltaic cells convert solar energy into usable electricity via a process called the ‘photovoltaic effect’.
The photovoltaic cell is composed of two different semiconductor materials –typically one layer of positively charged silicon and one layer of negatively charged silicon– that are joined together to create an electric field. When sunlight strikes the cell, electrons from the silicon atoms come loose, and are set into motion by the electric field. The motion of these electrons creates an electrical current.
The electricity that is generated from the cell is called a direct current (DC), which is incompatible with homes. Therefore, an inverter converts the direct current into an alternating current (AC). This AC electricity runs through the electrical panel, and can be used to power appliances in the same way that electricity generated from the electrical grid can.
Watch this video for a more visual explanation of photovoltaic cells!
2. Solar thermal systems
Another method of harnessing solar energy is via solar thermal systems. Solar thermal systems capture heat energy from the sun. The heat energy can be used directly for heating, and/or the production of electricity.
Heating
Solar thermal systems that capture heat energy for heating purposes can be passive or active.
Passive systems are very basic with no moving component parts, instead relying on design features to capture the sun’s rays. For example, solar ovens and greenhouses.
Active systems, however, are more complex with mechanical components such as fans and pumps to circulate heat carrying fluids. These systems can be used to heat homes and commercial buildings.

Solar oven. [Image sourced from EcoBusiness].
Electricity production
The solar thermal system that uses solar heat energy for electricity production is known as ‘Concentrated Solar Power’ (CSP).
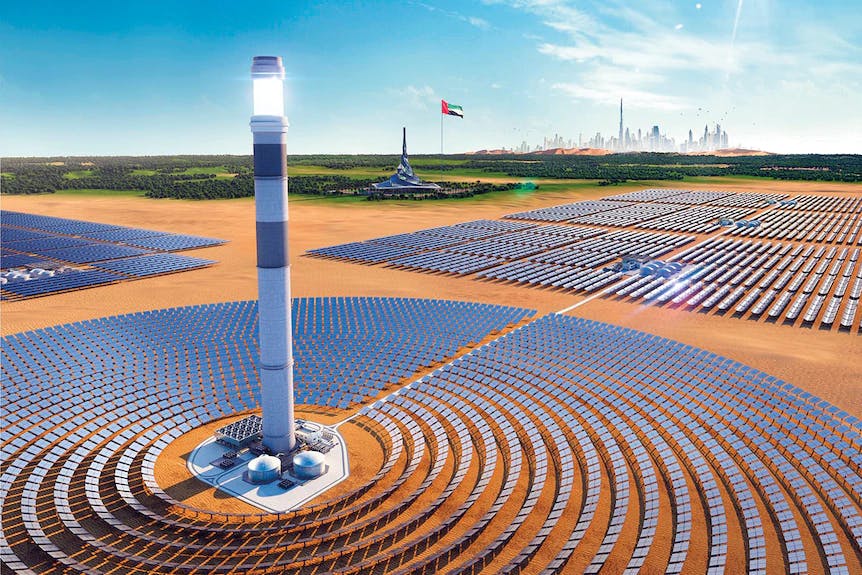

Concentrated Solar Power system. [Image sourced from abc news au].
CSP is a system consisting of numerous mirrors, that reflect and concentrate solar energy onto a central collector, generating high temperatures and producing steam. The steam turns a turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity. CSP’s are often situated in remote locations that are spacious and receive plentiful sunlight, such as deserts.
There are several types of CSP systems, such as the power tower (pictured above), parabolic trough, linear fresnel, and parabolic dish systems. For each of these, there are various design configurations depending on thermal energy storage.
To learn about the different types of CSP in more detail, read here!
Is solar power popular?
The short answer is yes, and increasingly so! As the awareness of climate change increases and the price of solar installation decreases, the use of solar power is on the rise.
Currently, the largest solar energy producer in the world is China, having installed over 170 GW of solar capacity in 2018, and aiming to achieve an estimated 370 GW of solar capacity by 2024.
The U.S. follows behind China with 85 GW of installed solar capacity reported in 2018. The U.S. offers a federal solar tax credit, and on top of this, individual states also offer very generous state incentives in order to make solar power affordable and support the industry’s shift to renewable energy consumption.
Other key players in the solar energy race include Japan (62 GW), Germany (45 GW), and India (31 GW), according to the International Renewable Energy Agency 2018 country rankings report.
Country Rankings for Solar Energy Electricity Generation: 2018.
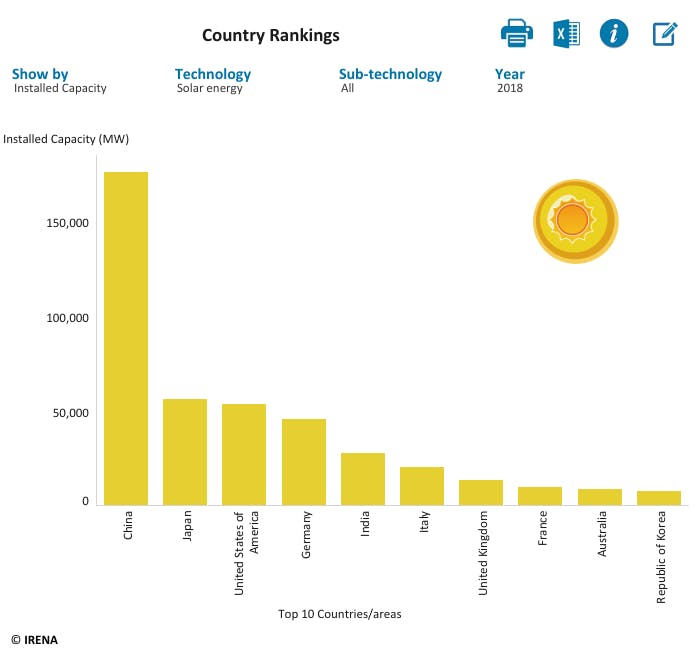
The top 10 country rankings for electricity generation by solar energy technology, in the year of 2018. [Sourced from the International Renewable Energy Agency].
Still curious?
To find out more about solar power, check out these informative links:
· National Geographic – What is solar power?
· How do industrial solar panels benefit businesses?
· Curious about U.S state incentives?
Stay up to date with more of Who’s Saving the Planet’s inspiring podcasts here!